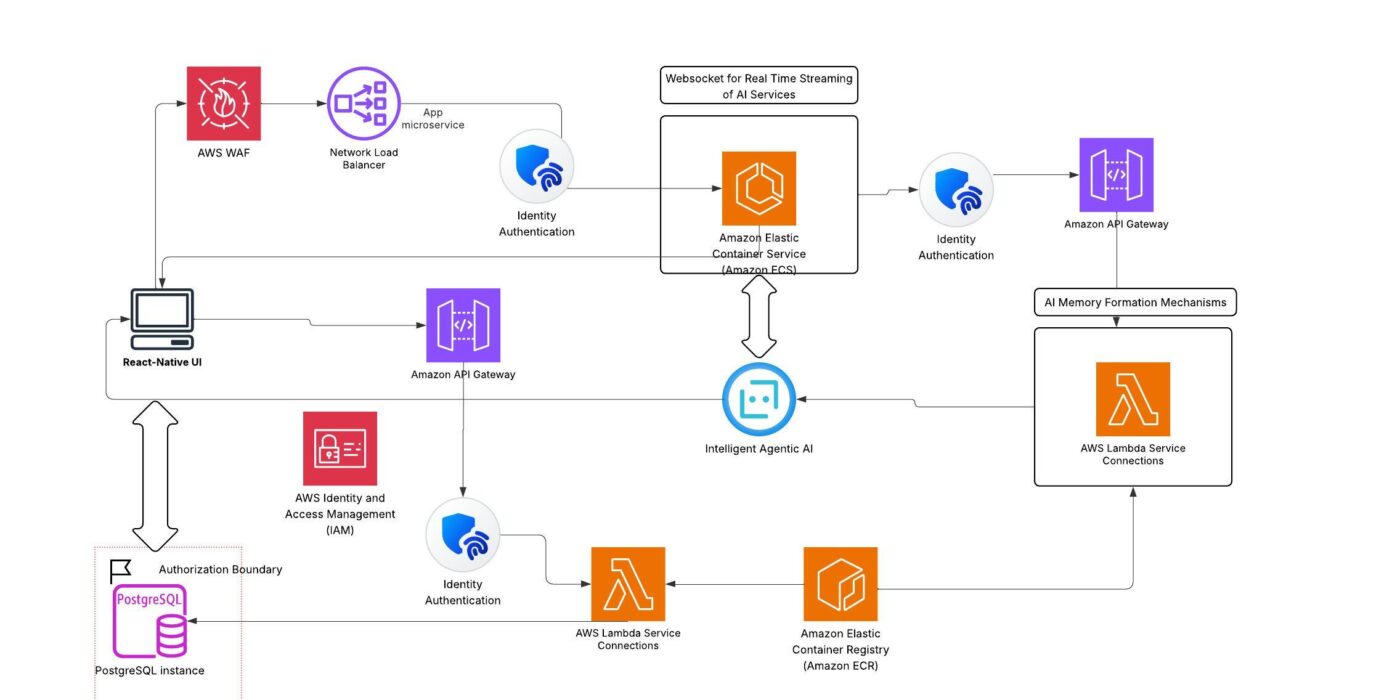
High-Level Architecture Summary
This architecture illustrates a secure, modular, and scalable AI-driven application built using Amazon ECS and a modern, cloud-native stack:
Cross-Platform Frontend:
The platform is anchored by a React Native UI, enabling a seamless experience for users across mobile and web devices. Secure authentication and authorization guard all user interactions and sensitive transactions.
API & Security Layer:
AWS WAF and API Gateway provide a robust entry point, protecting against threats and efficiently routing traffic to backend services. AWS IAM is leveraged to enforce strict identity and access management across all resources.
AI Compute & Real-Time Processing:
Core application logic and AI workflows run on Amazon ECS using the Fargate launch type, allowing for secure, serverless, and on-demand container execution. Real-time features and intelligent agent interactions are enabled through WebSocket connections for responsive, interactive experiences.
Automation & Orchestration:
AWS Lambda functions are used for background automation, scheduled tasks, service connections, and orchestration of complex workflows, including AI-driven memory mechanisms and asynchronous processing.
Data Management with Supabase:
Persistent application data is managed by Supabase, utilizing its scalable PostgreSQL backend. The architecture ensures secure, authorized data flow between services and upholds compliance through well-defined authorization boundaries.
Container Lifecycle & CI/CD:
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) is used for the storage and deployment of application containers, supporting continuous integration and delivery pipelines for rapid, reliable deployment of microservices and AI components.
Integrated Modular Design:
By combining Amazon ECS for scalable compute, Supabase for data management, and AWS managed services for orchestration, security, and deployment, the system is positioned for high reliability, operational flexibility, and ongoing innovation.
Additionally, GitHub Actions has been configured to automate the deployment workflows for all repositories in this project, ensuring streamlined, continuous integration and delivery across all system components. A high level look at SOME of the user interfaces for the application will now be shown.
Web Application




React-Native IOS/Android Application
This application was built using the React Native framework in TypeScript/JavaScript. React Native enables rapid development of high-quality, cross-platform mobile applications using a single codebase. By leveraging React Native, the app delivers a native user experience on both iOS and Android devices, while benefiting from a robust ecosystem and seamless integration with modern JavaScript tooling.

A series of images will be shown capturing some of the screens and some of the main features of the app themselves. Note that the service integrations, sign ups, and AI Hub are not shown in the following.
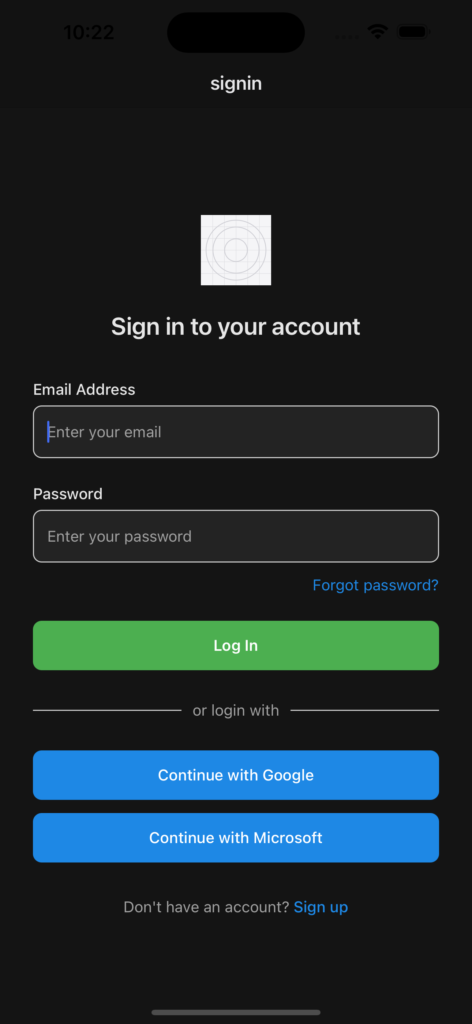
The application includes a streamlined sign-up process designed to make onboarding quick and secure. In addition to traditional registration, users can sign up directly using their Google accounts—making authentication simple and convenient. This direct Google authentication is one of several user-friendly features integrated into the platform.

The Home Screen features an AI agent and displays upcoming events synced from Google, iOS, or other external calendars.

This screen features the AI agent chatbot. Notice that this chatbot has personalized and actual has information about my profile. Additionally, as the user interacts with the AI agent, more information will be collected and the AI agent will be more and more personalized. This screen features the AI agent chatbot, which is personalized with information from your profile. As you interact with the AI agent, it continually gathers more insights, allowing for an increasingly tailored experience.

This is the calendar view of a user’s events. Very standard calendar with navigation between months. Note that there are additional weekly and daily views for this calendar not being shown. To switch to those views, you would open the calendar menu by clicking the calendar icon in the top right hand corner of the image. This is the calendar view, displaying a user’s events in a familiar monthly format with intuitive navigation between months. Additional weekly and daily views are also available (not shown here). To switch views, simply open the calendar menu by clicking the calendar icon in the top right corner.

This is the connect external services drawer menu that is opened when you toggle the three lines icon in the top left hand corner of the previous image. When clicking on these icons, you will be redirected to the appropriate workflows which will then import all calendar data you have for the respective service.

The final image highlights the profile settings page, where users can view their basic information and check the status of connected calendars. While password change functionality is planned for future updates, it is not yet implemented.
Conclusion
In summary, this React Native app—integrated with Amazon Web Services—provides a robust, scalable foundation for intelligent event management and user interaction. While the project is largely complete and fully functional, there remains room for minor refinements to further enhance the user experience.